millon's test for protein|Millon’s Test – Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses : Pilipinas Millon’s test (Cole’s test) Test For Detection of Tyrosine. Principle: Millon’s test is specific test for identification of tyrosine. Tyrosine containing protein when reacts . Looking for online definition of PCSO or what PCSO stands for? PCSO is listed in the World's most authoritative dictionary of abbreviations and acronyms The Free Dictionary
millon's test for protein,Millon’s test is an analytical test used for the detection of the amino acid tyrosine, which is the only amino acid containing the phenol group. Millon’s test is a specific test for tyrosine, but it is not a specific test for protein as it also detects the phenolic group present in other compounds as well. Therefore, . Tingnan ang higit paMillon’s test is based on the principle of nitrification of the phenol group in tyrosine, which then forms complexes with heavy metals like . Tingnan ang higit pa Millon’s test is one of the qualitative methods to determine differences in types of proteins and amino acids, namely the type of phenolic amino or amino acids . Millon’s test (Cole’s test) Test For Detection of Tyrosine. Principle: Millon’s test is specific test for identification of tyrosine. Tyrosine containing protein when reacts . Millon’s test can be described as an analytical test for the identification that the amino acid tyrosine which is the sole amino acid with the phenolic group. Millon’s .
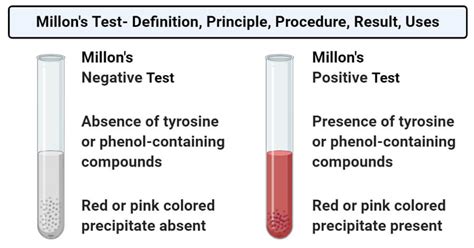
Millon’s test is given by proteins containing phenolic amino acids. Gelatin does not give this test. First, a white precipitate is formed when proteins are treated with millions reagent and then turns to brick-red .millon's test for protein Millon’s Test – Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses Principle of Millon’s test: Compounds containing hydroxybenzene radical react with Millon’s reagent to form red complexes. The only amino acid having hydroxybenzene ring is . Millon’s test can be described as an analytical test for the identification that the amino acid tyrosine which is the sole amino acid with the phenolic group. Millon’s .Millon's reagent is an analytical reagent used to detect the presence of soluble proteins. A few drops of the reagent are added to the test solution, which is then heated gently. A .Millon’s test is used for the detection of amino acid tyrosine. REAGENTS: Millon’s Reagent: Mixture of mercurous and mercuric nitrates. PRINCIPLE: The mercurous and .
Millon’s Test is a chemical test used to detect the presence of protein (tyrosine and tryptophan) in a given sample.Millon’s test is given by proteins containing phenolic amino acids. Gelatin does not give this test. . If there is formation of yellow precipitate then the presence of protein is confirmed. (c) Millions Test: Take 2ml of . Result and Interpretation of Millon’s Test. Positive result:A red or pink-tinted precipitate forming during the Millon’s test is indicative of a favourable outcome. This indicates the presence of tyrosine or a protein having tyrosine. Negative result:The lack of coloured precipitate in the test tube shows that the Millon’s test was negative. Plants, due to the large quantities of carbohydrates that make up their structure, contain lower amounts of protein compared to animal cells . However, the vegetal food production has a lower environmental footprint than animal husbandry. . Millon’s test (for proteins)–Millon’s reagent (2 mL) was added to the extract (2 mL) and heated . Uses of Millon's Reagent. 1. Millon’s test is employed to detect tyrosine-containing proteins in an exceedingly given sample. 2. The test conjointly helps in the differentiation of amino acids from one another. 3. The test is helpful in the detection of casein macromolecules and also the macromolecules found in meat. Millon’s test can be described as an analytical test for the identification that the amino acid tyrosine which is the sole amino acid with the phenolic group. Millon’s test is a particular test for tyrosine; however, it’s not a specialized test for protein since it also detects the phenolic component found in other substances as well.

Millon’s test can be described as an analytical test for the identification that the amino acid tyrosine which is the sole amino acid with the phenolic group. Millon’s test is a particular test for tyrosine; however, it’s not a specialized test for protein since it also detects the phenolic component found in other substances as well.
Edited By: Sagar Aryal. Biuret Test is the test used to detect the presence of peptide bonds in the sample and to test for the presence of proteins or peptides. Proteins and peptides are polymers of amino acids. They are chains of amino acids as well as other biomolecules or ions or compounds. The amino acids are covalently bound to each other . Some of the qualitative methods that are used to detect different types of proteins and amino acids are Ninhydrin test, Xanthoproteic test, Millon's test, Sulfur test, Hopkins-Cole test, and .
Procedure: Add 1 ml of the unknown protein solution into a test tube. Add 1 ml of Millon’s reagent to the test tube. Mix the contents of the test tube thoroughly using a dropper. Heat the test tube in a water bath at 56°C for 10 minutes. Allow the solution to reach at the room temperature. Observe the color of the solution.
1. Millon's Test. Millon's test is given by any compound containing a phenolic hydroxy group. Consequently, any protein containing tyrosine will give a positive test of a pink to dark-red colour. The Millon reagent .

There are six tests for the detection of functional groups in amino acids and proteins. The six tests are: (1) Ninhydrin Test (2) Biuret Test (3) Xanthoproteic Test (4) Millon’s Test (5) Hopkins-Cole Test and (6) Nitroprusside Test. We divide the food we consume into three main classes: carbohydrates, the body’s most readily available .The Millon’s test is a specific test for tyrosine, but it is not a specific test for protein as it also detects the phenolic group present in other .
Millon’s Test – Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses Millon’s test is a particular test for tyrosine; however, it’s not a specialized test for protein since it also detects the phenolic component found in other substances as well. So, when conducting the Millon test it is vital to perform other tests, such as the Biuret test as well as the Ninhydrin test are also performed. .
Test sample, Millon’s reagent. Procedure Take 2 ml of test sample and add 2 ml Millon’s reagent in it. Then boil it for 2-5 minutes in water bath to develop red color pre-cipitate. Observation of red colored precipitates indicates presence of protein in the test solution. However, excess of reagent produces Millon’s test can be described as an analytical test for the identification that the amino acid tyrosine which is the sole amino acid with the phenolic group. Millon’s test is a particular test for tyrosine; however, it’s not a specialized test for protein since it also detects the phenolic component found in other substances as well.millon's test for proteinThe presence of protein can also be detected using Millon’s reagent. Millon’s reagent reacts with tyrosine amino acids, common to most proteins, and results in the formation of a reddish-brown precipitate when heated. The table below summarises the major tests and their expected results in the presence and absence of protein.Millon’s test is a specific test for tyrosine, but it is not a specific test for protein as it also detects the phenolic group present in other compounds as well. Therefore, while performing Millon’s test, it is essential that other tests like the .
millon's test for protein|Millon’s Test – Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
PH0 · Test for Protein
PH1 · Millon’s test: Principle, Reaction, Reagents, Procedure
PH2 · Millon’s test: Objective, Principle, Reagents,
PH3 · Millon’s test – Its Principle, Reagents, Procedure etc
PH4 · Millon’s Test: Qualitative Identification of Proteins
PH5 · Millon’s Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure And Result
PH6 · Millon’s Test: Objective, Principle, Procedure And Result
PH7 · Millon’s Test – Definition, Principle, Procedure, Result, Uses
PH8 · Millon's reagent
PH9 · Millon's Test